Inhibiting Messages
Ignore Message
Suppressing a message at a specific location can be achieved with the Ignore Message XY at this location quickfix. This will insert a //lint !eXYZ comment at the correct position in the sourcecode.
Inhibit Lint Messages
Lint provides various options to inhibit messages, as described in Section 5 of the Lint manual. These options can be specified manually in a custom lint file, but Linticator can also generate the correct inhibition option for you.
The inhibition wizard can be invoked from any position in the source code that contains a Lint marker:
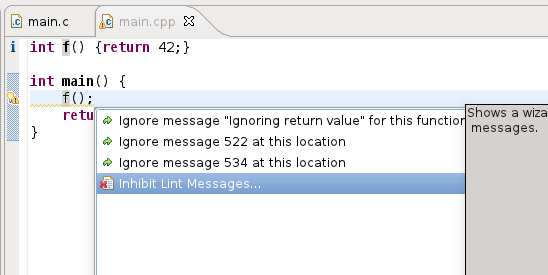
A wizard will then offer you several inhibition options.
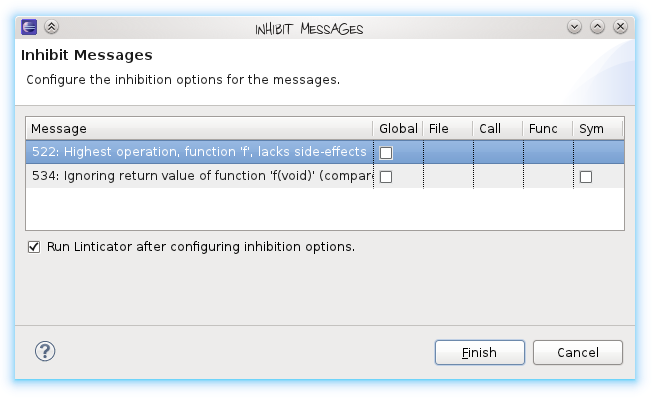
Depending on the concrete Lint message, one or more option can be selected:
Global
Writes a @-eXYZ@ inhibition option which inhibits message XYZ for the whole project.
File
Messages that are about (not in) a file can be suppressed with this option. Linticator will write a -efile(XYZ, filename) inhibition directive.
Call
Messages that occur in the context of a function call, that is, while the function call or one of its arguments is being parsed. Linticator will generate a -ecall(XYZ, functionname) inhibition option.
Func
The Func inhibition option can be used to inhibit a message that occurs within a function. Linticator writes a -efunc(XYZ, function) option to suppress this message type.
Sym
Sym is often the most useful option; it can inhibit a message about a certain function or name (Lint messages parametrized with ‘Symbol’ or ‘Name’). This creates a -esym(XYZ, symbolname) option.
After finishing the wizard and re-linting the project, the now inhibited messages will not show up again.
Ignore Function Return Value (Lint message 534)
If one chooses to ignore a specific function’s return value, chances are that other calls to that function are also allowed to ignore the return value, so this quickfix simply suppresses message 534 for this specific function for the whole project.
This is achieved with an -esym(534, <function>) entry in the options file. All such excluded functions can be seen in the project’s Linticator properties page.
std::vector in, out;
std::copy(in.begin(), in.end(), out.begin()); // 534 Ignoring return value of function 'std::copy(...
</code></pre>
# Quickfixes
Note that quickfixes are only available for Eclipse Helios and never releases.
## Cast Assigned Expression (Lint message 64)
Inserts a static_cast for type mismatches in assignments:
void *v;
int *i;
i = v; // 64: Type mismatch (assignment) (ptrs to void/nonvoid)
The quickfix changes this into
void *v;
int *i;
i = static_cast<int *>(v);
## Create Include Guard (Lint message 451)
A header file that is included multiple times should be protected by an include guard. This quickfix generates an appropriate include guard for this header file.
/* this header does not have an include guard */
int someFunction(void);
becomes
#ifndef HEADER_FILE_H_
#define HEADER_FILE_H_
/* this header does not have an include guard */
int someFunction(void);
#endif /* HEADER_FILE.H_ */
## Remove Unused Variable (Lint message 529)
Removes a local variable declaration that is never referenced:
void f() {
int unused; // 529: Symbol 'unused' (line 2) not subsequently referenced
}
void f() {
}
## Add Return Statement (Lint message 533)
This quickfix adds a return statement with a default-constructed value at the end of a function.
std::string shouldReturn() {
if(someCondition) {
return "Hello";
}
} // 533: function 'shouldReturn(void)' should return a value
becomes
std::string shouldReturn() {
if(someCondition) {
return "Hello";
}
return std::string();
}
## Cast Relational Expression To Matching Type (Lint message 574)
Applying one of the relational operators (<, <=, >=, >) to mixed sign/unsigned arguments triggers message 574, which can be fixed by a cast:
int i = -3;
unsigned int j = 20;
if(i < j) {
}
becomes
int i = -3;
unsigned int j = 20;
if(i < static_cast(j)) {
}
</code></pre>
## Declare Virtual (Lint message 1093)
Declaring a non-virtual function pure (.. } = 0) is an error and can quickly be fixed:
class Faulty {
public:
Faulty();
virtual ~Faulty();
void shouldBeVirtual() = 0; // A pure specifier was given for function 'Faulty::shouldBeVirtual(void)' which was not virtual
};
becomes
class Faulty {
public:
Faulty();
virtual ~Faulty();
virtual void shouldBeVirtual() = 0;
};
## Include TypeInfo (Lint message 1405)
When using the typeid function, the corresponding header file should be included:
#include
int main() {
std::cout << typeid(int).name() << std::endl; // 1405: Header must be included before typeid is used
}
</code></pre>
becomes
#include
#include
int main() {
std::cout << typeid(int).name() << std::endl;
}
</code></pre>
## Declare Member Function Const (Lint message 1762)
Makes a member function const by adding the const keyword to both declaration and definition:
struct Const {
int couldBeMadeConst() {
return 42;
} // 1762: Member function 'Const::couldBeMadeConst(void)' could be made const
};
becomes
struct Const {
int couldBeMadeConst() const {
return 42;
}
};
## Declare Reference Parameter Const (Lint message 1764)
Whenever possible, reference parameters should be made const:
struct Class {
std::string couldHaveConstRefParameter(std::string& s) const {
return s;
} // 1764: Reference parameter 's' (line 4) could be declared const ref
};
becomes
struct Class {
std::string couldHaveConstRefParameter(const std::string& s) const {
return s;
}
};